Table of Contents
What is an Autoimmune Disease?
Autoimmune Diseases – Type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis: about a hundred different autoimmune diseases. What do they have in common? All of them are the result of a dysfunction of the immune system.
Typically, it recognizes the body’s cells and does not attack them, just repelling external agents like viruses and bacteria. In autoimmune diseases, certain parts of the immune system (antibodies or T lymphocytes) directly attack cells and their components as foreign elements. This abnormal reaction leads to inflammation and various symptoms, affecting organs.
Long considered rare, autoimmune diseases affect 3 to 5% of the population and generally affect ten times more women than men. Most of these diseases are due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors, but the mechanisms remain poorly understood.
Some researchers believe that these illnesses may be the price of having a solid defence system against infection. That was suggested in 2016 by a researcher in evolutionary biology at Princeton University, who analyzed data collected from 1000 people born in Taiwan between 1892 and 1953. Results: those who had the most autoantibodies, these self-attacking antibodies, were the ones that lived the longest.
What are the causes of Autoimmune Disease?
Auto is a medical term that means self. The immune system is the body’s defence system. It helps protect the body against disease and infection. The immune system usually attacks bacteria, viruses and cancer cells that invade it. In autoimmune diseases, a person’s immune system attacks tissues in their own body.
There are many different Autoimmune Diseases.
- Doctors do blood tests for autoimmune disease
- They treat autoimmune diseases with drugs that slow down the immune system
- Autoimmune diseases can attack virtually any part of the body: Here are some points
- Blood cells ( autoimmune hemolytic anaemia)
- Blood vessels ( vasculitis )
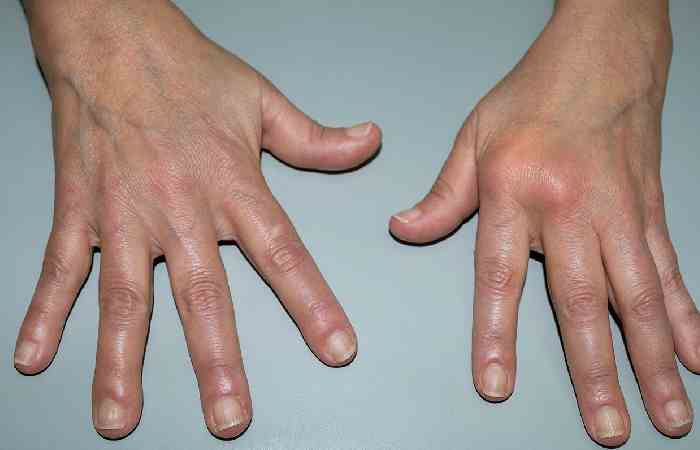
- Joints ( rheumatoid arthritis )
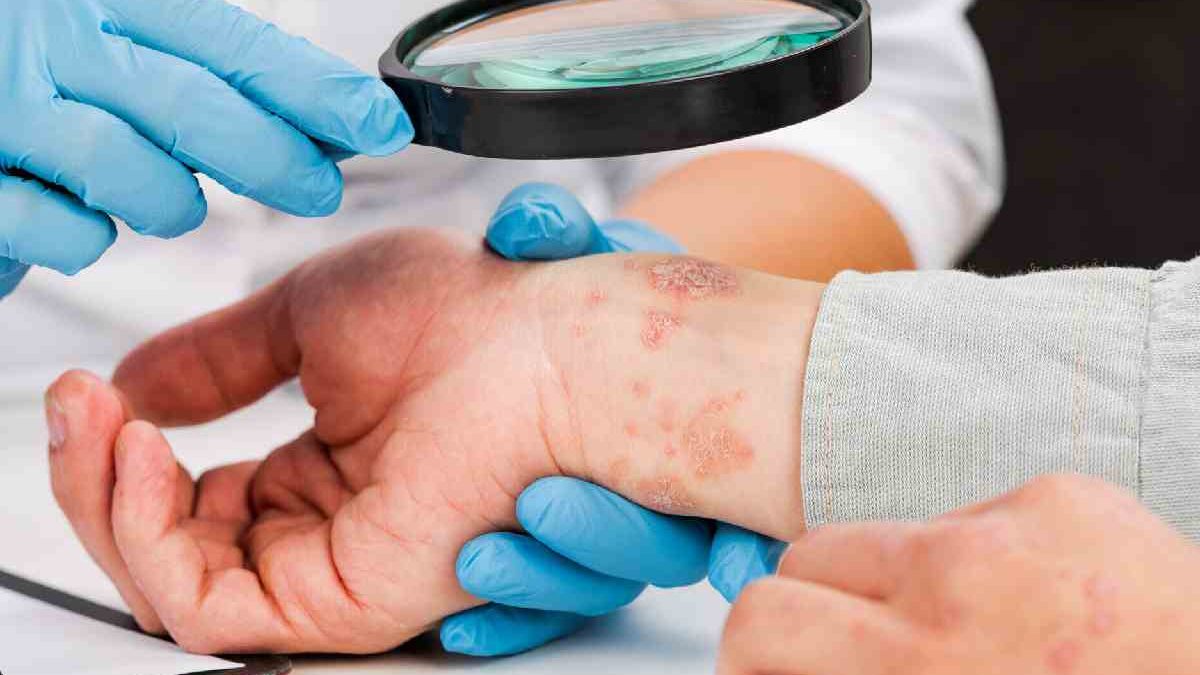
- Skin (lupus, bullous pemphigoid or vulgar pemphigus )
- Lungs and kidneys ( Goodpasture syndrome or lupus)
- Brain and spinal cord ( multiple sclerosis )
- Thyroid (Graves disease or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis )
- Pancreas ( type 1 diabetes )
What stay the symptoms of an Autoimmune Disease?
Symptoms vary depending on the disease and the part of the body affected. However, in general, autoimmune diseases cause tissue swelling and damage. You may have one or more of these symptoms:
10 Symptoms Of Autoimmune Disease
- Painful joints
- Swollen and red joints
- Itching
- Fever
- Diarrhoea
- Tired
- Inflamed eyes
- Colonoscopy
- Joint puncture
- Skin problems
What types of Autoimmune Diseases?
Your immune system preserves you from disease and infection by attacking germs that enter your body, such as viruses and bacteria. Your immune system can tell germs are not part of you, so it extinguishes them. If you take an autoimmune disease, your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in your organs and tissues.
There are above 80 types of autoimmune diseases. They can affect almost any part of your body. For example, alopecia areata is an autoimmune skin disease that causes hair loss. Autoimmune hepatitis affects the liver. In type 1 diabetes, the immune system attacks the pancreas. And in rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system can attack many parts of the body, including the joints, lungs, and eyes. What are the causes of autoimmune diseases?
No one knows why these diseases occur. But you can’t get them from other people. Autoimmune diseases tend to be familial, which means that specific genes make some people more likely to develop a problem. Viruses, certain chemicals and other things in the environment can trigger an autoimmune disease if you already have the genes.
Who is at risk for Autoimmune Diseases?
However, Millions of Americans of all days suffer from autoimmune diseases. Women develop many types of diseases much more often than men. And if you have one autoimmune disease, you’re more likely to get another. Symptoms of autoimmune disorders can come and go. During a relapse, your symptoms may get worse for a while. Later, you may go into remission, which means your symptoms get better or go away for a time.
How are Autoimmune Diseases Diagnosed?
Doctors often have trouble diagnosing it. There is usually no specific test to show if you have a particular autoimmune disease. And the symptoms can be confusing. That is because many of it have similar symptoms. And specific symptoms, such as muscle pain, are common in many other illnesses. So it can take a long time and a few visits to different types of doctors to get a diagnosis.